India Location And Extent

World Continents
September 14, 2019

India – Animal Sanctuary
October 12, 2019When asked by the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, “How does India look from the space?” – “SaareJahaan se Accha (best in the world)” was the reply of the first Indian cosmonaut Rakesh Sharma. India does look beautiful from up there.
It has a crown like Kashmir, Bay of Bengal in East, the Arabian Sea in West and Adam’s bridge (Rama-Setu bridge) in South. Let’s understand in details the size and location of India.
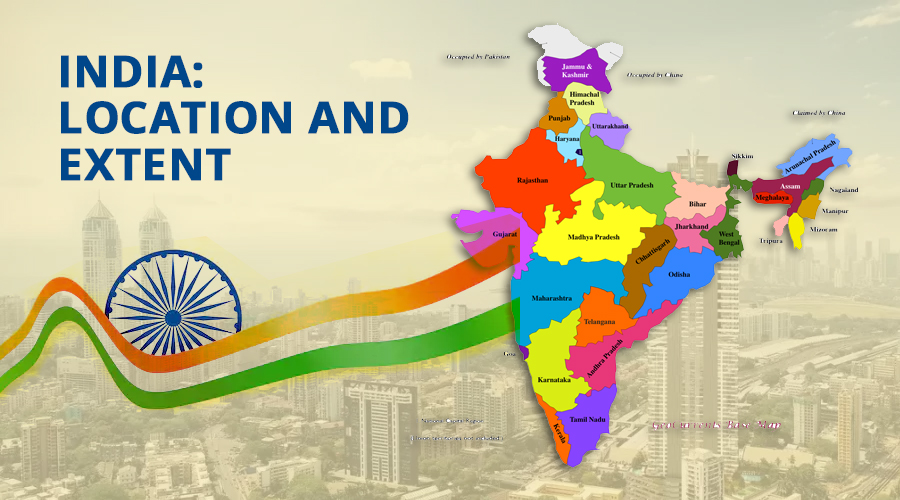
India also known as Bharat is a geographical unit with its own uniqueness. It covers an area of 3.28 million sq. km. It is the seventh largest country in the world. India covers about 2% of the world’s total area.
Location and Extent:
- India occupies the south-central peninsula of Asian continent.
- Himalayan mountain ranges separate Indian sub-continent from rest of Asian continent.
- Indian sub-continent includes India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Maldives, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh.
- On the southern side India has two water bodies namely Bay of Bengal on the western side and Arabian Sea in the Eastern side.
- Our country also includes two island groups Andaman and Nicobar Islands in Bay of Bengal & Lakshadweep islands in Arabian Sea.
- India is strategically located on the international trade route connecting eastern and western hemispheres.
- The mainland of India extends between 8°4ˈ and 37°6ˈ North Latitude and 68°7ˈ and 97°25ˈ East longitude.
- Tropic of Cancer 23°30ˈ N, divides India into almost two equal halves. So, India lies in tropical and sub-tropical zones of Northern hemisphere.
- From (Kashmir to Kanyakumari) i.e., north to south India covers a distance of about 3214 km.
- From (Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh) i.e., East to West India covers 2933 km.
- India has a land frontier of 15200 km and a coast line of about 7516.6 km.
- There is a lot of time difference between the eastern and western extremes of the country because of great longitudinal extent.
- The difference in local time between eastern and western hemispheres is about two hours.
- To avoid confusion from this vast time difference, 82°5ˈ E longitude located in Mirzapur is taken as standard reference point.
- This reference point is called standard time of India or Indian Standard Time (IST).
- It is important to note that India does not observe Day light Saving time (DST).
Indian standard time (IST)
- We all know that Earth is divided into 360 vertical lines or longitudes.
- A shift in every longitude gives a time difference of 4 minutes and with a longitudinal shift of 15 degrees, there is a time difference of 60 minutes/1 hour.
- In India, the longitudinal difference between India’s easternmost point Kibithu in Arunachal Pradesh and the westernmost point Gugariyana, Gujarat is nearly 30 degrees. And so, there is a time difference of two hours.
- So, the Central Meridian of India is 82.5° East longitude which runs from north to south through the city of Allahabad (Mirzapur) is taken as the standard reference point. The local time of this central meridian is used for calculating the Indian Standard time (IST).
- It is usually 5½ hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time of the world.
- The 0° meridian passes through Greenwich in England. Each degree of the meridian accounts for four minutes of time and that the difference between Greenwich and Indian standard time is 82.5° x 4 = 330 minutes which is 5.5 hours.
The neighbours of India:
| Neighbour Country | Border Indian states |
|---|---|
| 1. Pakistan |
Gujarat Rajasthan Punjab Jammu & Kashmir |
| 2. Afghanistan | Jammu & Kashmir |
| 3. China |
Jammu & Kashmir Himachal Pradesh Uttarakhand Sikkim Arunachal Pradesh |
| 4. Nepal |
Uttarakhand Uttar Pradesh Bihar West Bengal Sikkim |
| 5. Bhutan |
Sikkim West Bengal Assam Arunachal Pradesh |
| 6. Myanmar |
Arunachal Pradesh Nagaland Manipur Mizoram |
| 7. Bangladesh |
West Bengal Assam Meghalaya Tripura Mizoram |
India and its boundaries:
The countries which border India are:
| Boundaries | Borders |
|---|---|
| North |
Bhutan Nepal China |
| West |
Pakistan Afghanistan |
| South | Palk Strait separates India and Sri Lanka |
| East |
Bangladesh Myanmar |
Names of boundary lines (in decreasing order of border length):
| Border Between | Border Name | Length |
|---|---|---|
| India-Bangladesh | Purbachal (operating zero line) | 4096.7 km |
| India-China | McMahon Line | 3380 km |
| India-Pakistan | Radcliffe Line | 3323 km |
| India-Myanmar | Indo-Burma barrier | 1643 km |
| India-Nepal | Radoliff Line | 1236 km |
| India-Bhutan | Indo-Bhutan border line | 699 km |
| India-Afghanistan | Durand Line | 106 km |
| India-Sri Lanka | Palk Strait | 30 km |


| The States that lie completely in the Himalayas |
Jammu and Kashmir Himachal Pradesh Sikkim Arunachal Pradesh Uttarakhand. |
|---|---|
| The States and the Union Territories that Cover Large Portions of the Great Northern Plains |
Punjab Haryana Uttar Pradesh Bihar West Bengal Assam |
| Union Territories |
Delhi Chandigarh Daman and Diu Pondicherry |
| The States that are made up of hills in N.E. India |
Arunachal Pradesh Nagaland Manipur Mizoram |
| The States that make up the Great Peninsular Plateau |
Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra Odisha Andhra Pradesh Karnataka Kerala Tamil Nadu Chhattisgarh |
| The States that form the Coast of India |
Gujarat Maharashtra Goa Karnataka Kerala Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh Odisha West Bengal |
The islands of India
India has a total of 247 Islands. Out of these 223 lie in Bay of Bengal and 24 lies in Arabian Sea.
| Islands | Description |
|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
They form two major groups in Bay of Bengal located between 10° and 14° N latitude. They are of volcanic origin and are formed of tertiary sandstone, limestone and shale. These Islands extend up to 8249 sq. km. |
| Great Nicobar Island |
These islands have an area of 862 sq. km is the largest island. It lies closest to the equator. |
| Lakshadweep Islands |
These islands have a total area of 32 sq. km. They are situated between 8° and 11° N latitudes. |
| Minicoy Islands | This island has an area of 4.5 sq. km |
| Other Important Islands |
Little Nicobar Katchall Camouta Trinkat Nan cowry Teressa Tivanchong |
Unity in Diversity:
- India has unique landscape ranging from the highest peaks to the lowest plains. Godwin Austin known as Mount K2 is the highest peak of India and the coastal plains are the lowest in the South.
- The climate varies from the tropical to the temperate zone. Cherrapunji in Meghalaya receives the highest amount of rainfall, whereas the Thar Desert receives the minimum rainfall.
- We have wet dense tropical forest in the Western Ghats, mangrove trees in the Sundarbans of West Bengal and Shrubs, and sparse vegetation in the Thar Desert.
- The diversity in the physical environment and climate has made India an ideal habitat of flora and fauna. Hence a wide variety of plants and animals are found in India.
- India is a secular country with total freedom of worship. People follow Hinduism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism and Zoroastrianism with cultural diversities.
- In spite of its physical, cultural, regional, religious and racial varieties India is known for unity in diversity because people forget their religious and linguistic differences and stand together during the time of crisis.
Interesting Facts:
- The sum of coastal length of all these states and union territories, the total coastal length of India becomes 7516.6 Km.
- India has 18th longest total coastal length among all world countries.
- The coastal length of mainland India (except Andaman & Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep islands) is 5422.6 Km.
- The coastal length of all islands taken together is 2094 Km.
- Pamban Island located between India and Sri Lanka has rocky surface.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands are the largest in terms of area where as Lakshadweep Islands are the smallest.
- India’s long coast line has added its contact with the world through its sea routes.